Innovative 3D Linkage Analysis for Advancing rAAV Studies in Gene Therapy
In recent years, recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) has become the vector of choice for in vivo gene delivery, showing promise in clinical trials for treating various human diseases. As rAAV-based therapies progress, precise quantification of the viral genome titer is essential to determine therapeutic dosage and ensure safety and efficacy. Traditional quantification techniques like quantitative PCR (qPCR) and single-channel droplet digital PCR (1D ddPCR) provide a foundation but have limitations – particularly in assessing the structural integrity of the viral genome. Conventional 1D ddPCR captures only partial information, targeting a single region of the genome, typically the therapeutic gene of interest (GOI), and lacks insight into whether the viral genome is intact or fragmented.
To address this challenge, our team developed an advanced 3D ddPCR assay that provides a more comprehensive analysis of rAAV genomes. By targeting three distinct regions – the viral genome’s two ends and the center of the GOI – we offer a multi-dimensional approach to measuring not just the quantity but also the quality of rAAV genomes. Understanding the integrity of AAV viral genome is critical to ensure the safety and efficacy of rAAV gene therapy product. Our method introduces a cutting-edge 3D digital PCR assay with a three-point linkage analysis that goes beyond the simple quantification.
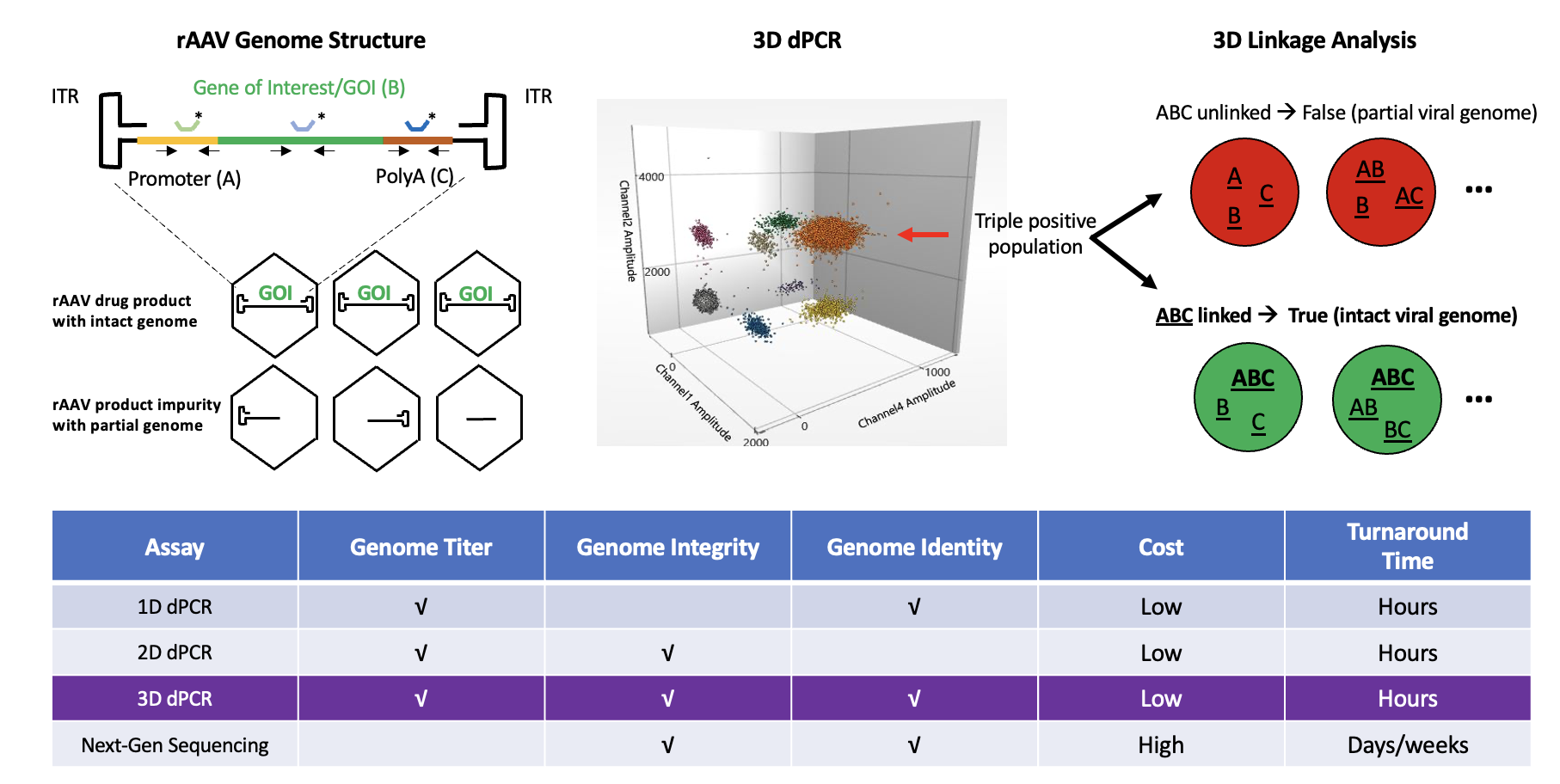
The random partitioning of DNA fragments in digital PCR means that even triple-positive droplets – those containing signals from all three targets – do not necessarily represent intact, full-length genomes. To overcome this, we developed a mathematical model that analyzes cluster data from the digital PCR results. This model accurately identifies true linked DNA molecules (intact genomes) while excluding false positives caused by co-partitioning of unlinked fragments. We validated this model through rigorous DNA mixing experiments, creating samples with known ratios of full-length and partial genomes. Our 3D linkage analysis showed high accuracy across multiple tests, demonstrating the reliability of our workflow in determining the percentages of intact genomes as well as partial fragments.
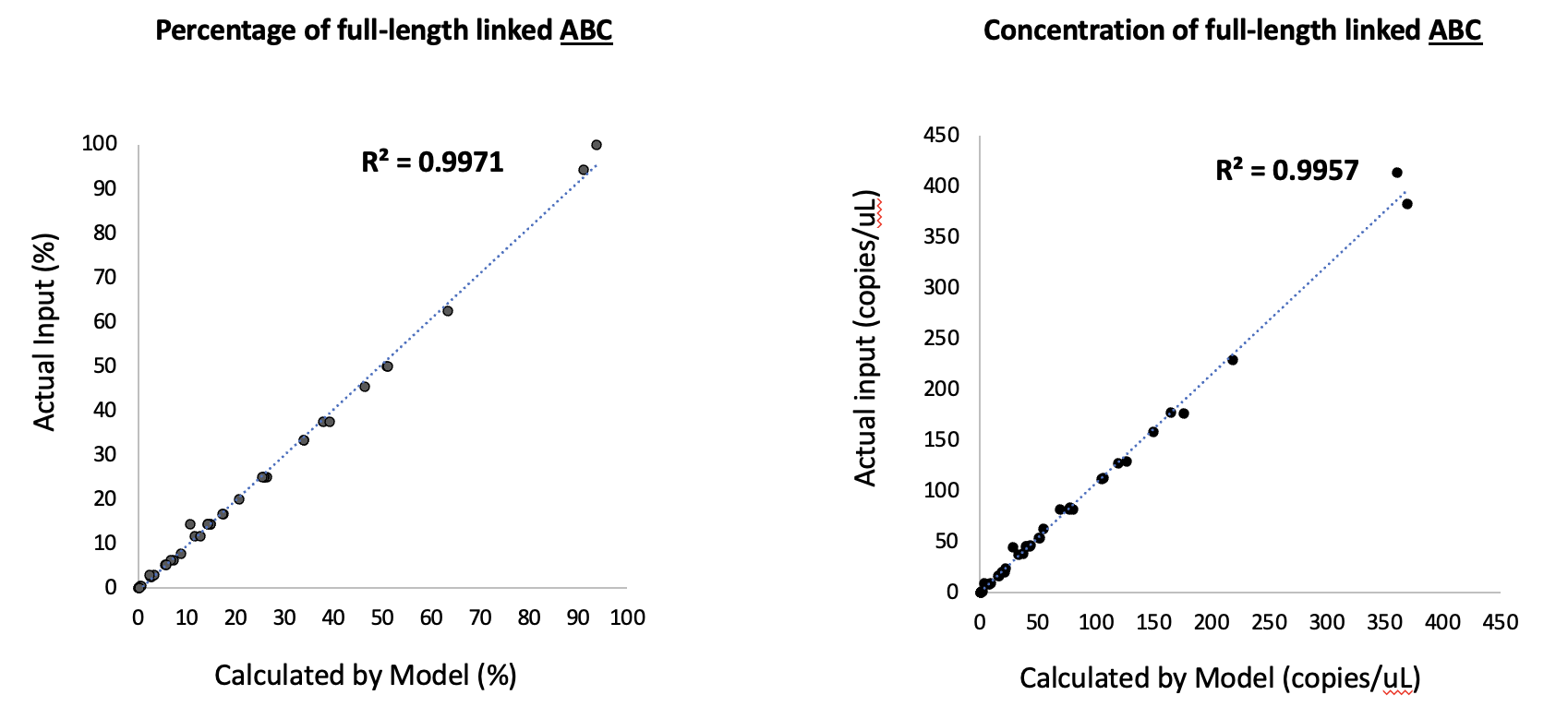
Our study not only confirms viral genome titer but also provides valuable information on genome integrity, making it a powerful tool for characterizing rAAV products in gene therapy. This innovative 3D digital PCR approach offers a cost-effective and straightforward setup similar to traditional 1D or 2D digital PCR with enhanced capabilities that are crucial for gene therapy applications. The insights gained from this method can help researchers and manufacturers develop safer and more effective rAAV-based treatments by ensuring that only high-integrity genomes are delivered.
In summary, our 3D digital PCR assay with linkage analysis is an important step forward in rAAV analytics. This technology not only allows for accurate quantification of viral genome titer but also offers comprehensive insights into genome integrity, setting a new standard for rAAV characterization in cell and gene therapy. This assay represents a promising avenue for improving the safety and efficacy of rAAV therapeutics and facilitating their broader adoption in clinical settings. Looking forward, we plan to make this 3D quantification assay widely accessible to the scientific community. We aim to do that through service and a digital portal (to be launched soon). To discuss how we can support your project, please contact us at licensing@lonza.com.
This research has been recently published in Scientific Reports journal – Three-dimensional linkage analysis with digital PCR for genome integrity and identity of recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus), please see publication for more details.